Declarative
A common pattern is for users to use Terraform to provision Kubernetes clusters perhaps using a Jenkins based pipeline. These brownfield clusters can then be imported into the controller.
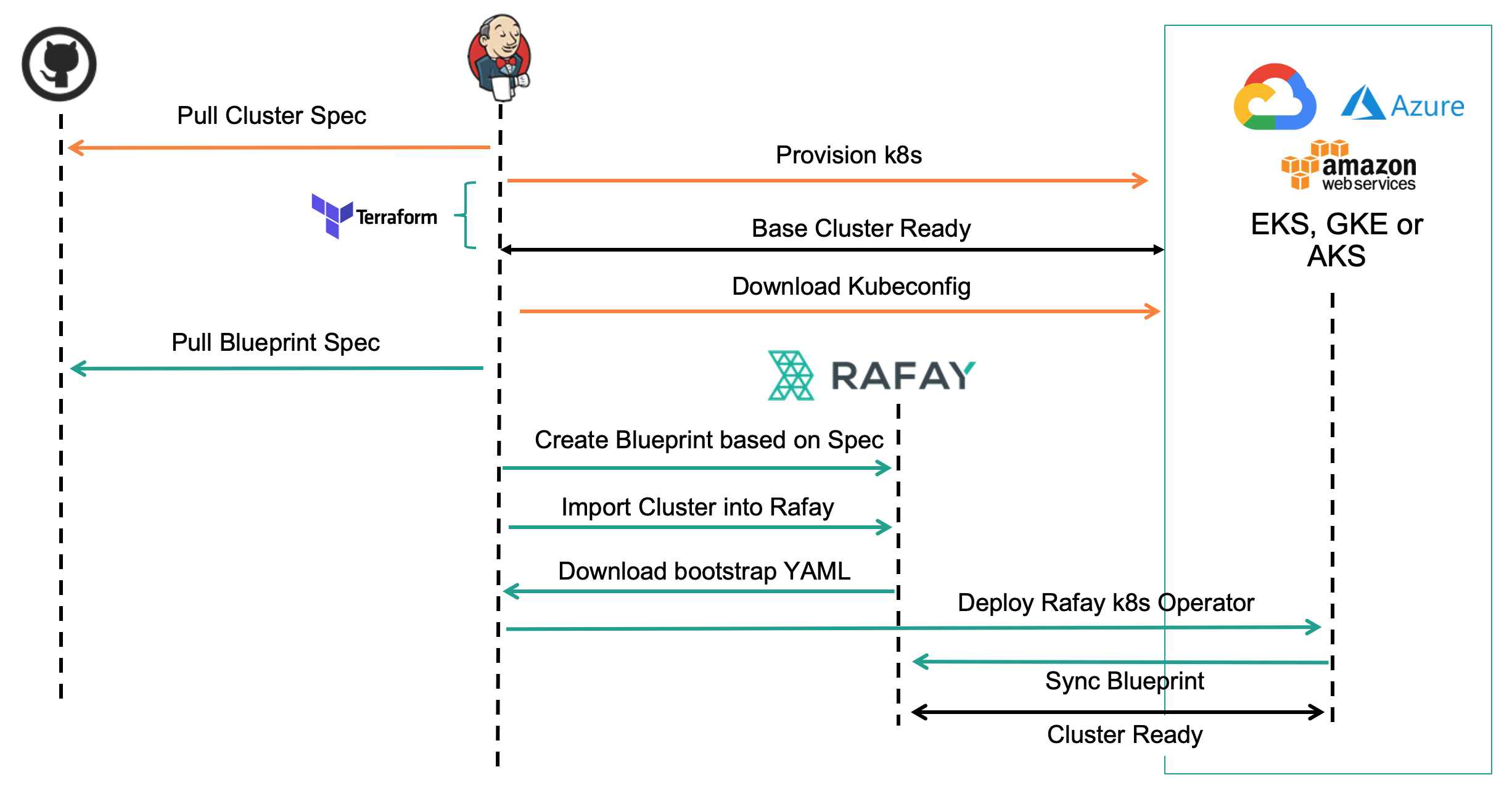
Typical Automation Sequence¶
The image below showcases a Jenkins based "pipeline" that automates the following steps.
- Uses Terraform to provision a Kubernetes cluster based on a version controlled cluster spec in a Git repo.
- Imports the raw Kubernetes cluster into the Controller
- Brings the cluster to a state of compliance with specified cluster blueprint.
Cluster Specification¶
Create and manage version controlled, declarative specifications for your clusters. Example cluster specifications are available in this public Git repo.
Create Cluster¶
To create the cluster on the controller with a cluster config file, use the following command:
./rctl apply -f <cluster config spec>
After creating the cluster, download the bootstrap YAML file for that cluster using the command:
./rctl get clusterbootstrap <cluster_name> > <cluster_bootstrap.yaml>
Apply the downloaded bootstrap YAML file to your existing clusters using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f <cluster_bootstrap.yaml>
Note: Ensure to replace
with the created cluster name.
Customers can seamlessly import their existing clusters into the controller using the provided specifications below. Depending on the cluster type, users can refer to the respective configurations outlined.
V3 Cluster Spec (Recommended)¶
AKS Cluster Import
For importing an existing AKS cluster, utilize the following configuration:
apiVersion: infra.k8smgmt.io/v3
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: demo-imported-v3-aks
project: demo
spec:
blueprintConfig:
name: minimal
config:
kubernetesProvider: AKS
location: azure/centralindia # Location: azure/centralindia (optional)
provisionEnvironment: CLOUD
proxyConfig: {}
type: imported
EKS Cluster Import
To import an EKS cluster, refer to the following configuration:
apiVersion: infra.k8smgmt.io/v3
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: demo-imported-v3-eks
project: demo
spec:
blueprintConfig:
name: minimal
config:
kubernetesProvider: EKS
location: aws/us-west-2 # Location: aws/us-west-2 (optional)
provisionEnvironment: CLOUD
proxyConfig: {}
type: imported
OnPrem Cluster Import
For importing an OnPrem cluster, use the following configuration:
apiVersion: infra.k8smgmt.io/v3
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: demo-imported-other1
project: defaultproject
spec:
blueprintConfig:
name: minimal
config:
kubernetesProvider: OTHER
provisionEnvironment: ONPREM
proxyConfig: {}
type: imported
Note: - provisionEnvironment supported values: CLOUD, ONPREM - kubernetesProvider supported values: AKS, EKS, GKE, OPENSHIFT, OTHER, RKE, EKSANYWHERE - Location is optional
V1 Cluster Spec¶
AKS Cluster Import
In the example below, the cluster will be provided a name "demo-cluster" in the Controller. It will be imported into the "defaultproject" and be provisioned with the "minimal" cluster blueprint.
apiVersion: rafay.io/v1alpha1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: demo-cluster
project: defaultproject
labels:
awsaccountid: demo_id
awsacmid: demo_id
env: devops
hostedzoneid: demo_id
region: us-west-2
spec:
blueprint: minimal
blueprintversion: Latest
location: azure/uksouth
cloudProvider: AKS
type: imported
List Clusters¶
To retrieve a specific imported cluster, use the below command
./rctl get cluster <importedcluster_name>
Output
./rctl get cluster demo-importedcluster
+------------------------+-----------+-----------+---------------------------+
| NAME | TYPE | OWNERSHIP | PROVISION STATUS |
+------------------------+-----------+-----------+---------------------------+
| demo-importedcluster | imported | self | |
+------------------------+-----------+-----------+---------------------------+
To retrieve a specific v3 cluster details, use the below command
./rctl get cluster demo-importedcluster --v3
Example
./rctl get cluster demo-importedcluster --v3
+------------------------+-------------------------------+-----------+----------+-----------+---------------------------+
| NAME | CREATED AT | OWNERSHIP | TYPE | BLUEPRINT | PROVISION STATUS |
+------------------------+-------------------------------+-----------+----------+-----------+---------------------------+
| demo-importedcluster | 2023-06-05 10:54:08 +0000 UTC | self | imported | | |
+------------------------+-------------------------------+-----------+----------+-----------+---------------------------+
To view the entire v3 cluster config spec, use the below command
./rctl get cluster <importedcluster_name> --v3 -o json
(or)
./rctl get cluster <importedcluster_name> --v3 -o yaml
Download Cluster Config¶
Use the below command to download an imported Cluster Config file
./rctl get cluster config <ClusterName> <ClusterConfigFileName.yaml>
Example:
/rctl get cluster config demo-imported demo-importedcluster-config.yaml
To download a v3 cluster config, use the below command
./rctl get cluster config <cluster-name> --v3
Important
Download the cluster configuration only after the cluster is completely provisioned
Delete Cluster¶
Already imported clusters can be deleted using the RCTL CLI. Note that this operation only deletes the cluster instance on the controller. The cluster administrator needs to manually delete the final remnants of the k8s operator on imported clusters.
rctl delete cluster <name of cluster>
Jenkins Example¶
Here is an example Jenkins pipeline to import an existing Kubernetes cluster into a specific project.