Part 2: Using Secrets
This is Part 2 of a multi-part, self-paced quick start exercise.
Note
This exercise requires MicroK8s and uses alias kubectl='microk8s kubectl'. If you do not have these already installed and running, see "Prerequisites".
What Will You Do¶
In part 2, you will:
- Use a Secret to store a password.
Estimated Time
Estimated time for this exercise is 5 minutes. Watch a video of this exercise.
Using Secrets¶
Kubernetes Secrets let you store and manage sensitive information, such as passwords, OAuth tokens, and SSH keys. Strong confidential information in a Secret is safer and more flexible than putting it verbatim in a Pod definition or in a container image.
Secret YAML file¶
Create a secret using a YAML file, which is a configuration file. You could create a YAML file from the command line, but for this exercise, you can just use a text editor. Or you can download the secret YAML file from this public Git repository.
- Open the Terminal.
- Navigate to the Downloads folder.
cd ./Downloads - Use the following command to create an empty YAML file in your Downloads folder.
touch secret.yaml - Use the nano text editor in the Terminal.
nano secret.yaml - Copy and paste the configuration below into the text editor.
- Press Cmd + X, then type Y and press Return to save the secret.yaml file.
- Open the command prompt.
- Navigate to the Downloads folder.
cd ./Downloads - Use the following command to create an empty YAML file in your Downloads folder.
copy NUL secret.yaml - Open the secret.yaml file with a text editor. For example, use Notepad++ to edit the YAML file.
- Copy and paste the configuration below into the text editor.
- Save the secret.yaml file.
- Open the Terminal.
- Navigate to the Downloads folder.
cd ./Downloads - Use the following command to create an empty YAML file in your Downloads folder.
touch secret.yaml - Use the nano text editor in the Terminal.
nano secret.yaml - Copy and paste the configuration below into the text editor.
- Press Ctrl + X, then type Y and press Enter to save the secret.yaml file.
Add a Secret¶
- In the Terminal or Command Prompt, add the secret to your environment using a YAML file.
kubectl create -f secret.yaml - List the secrets.
kubectl get secrets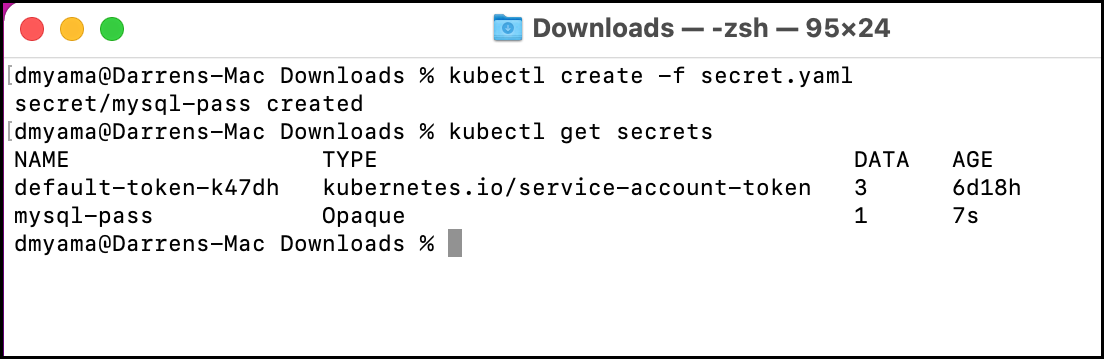
secret.yaml¶
This YAML file contains: - A metadata name, mysql-pass, that is used in the MySQL and WordPress deployments. - A type set to Opaque, which means it is arbitrary, user-defined data. - A password, admin123, that is encoded in base64.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysql-pass
type: Opaque
data:
password: YWRtaW4xMjM= # echo -n "admin123" | base64 -