Examples
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) is a flexible and powerful access control model that provides a granular level of control over access to resources. To illustrate the effectiveness of ABAC, let's explore some examples that demonstrate its practical applications in different scenarios.
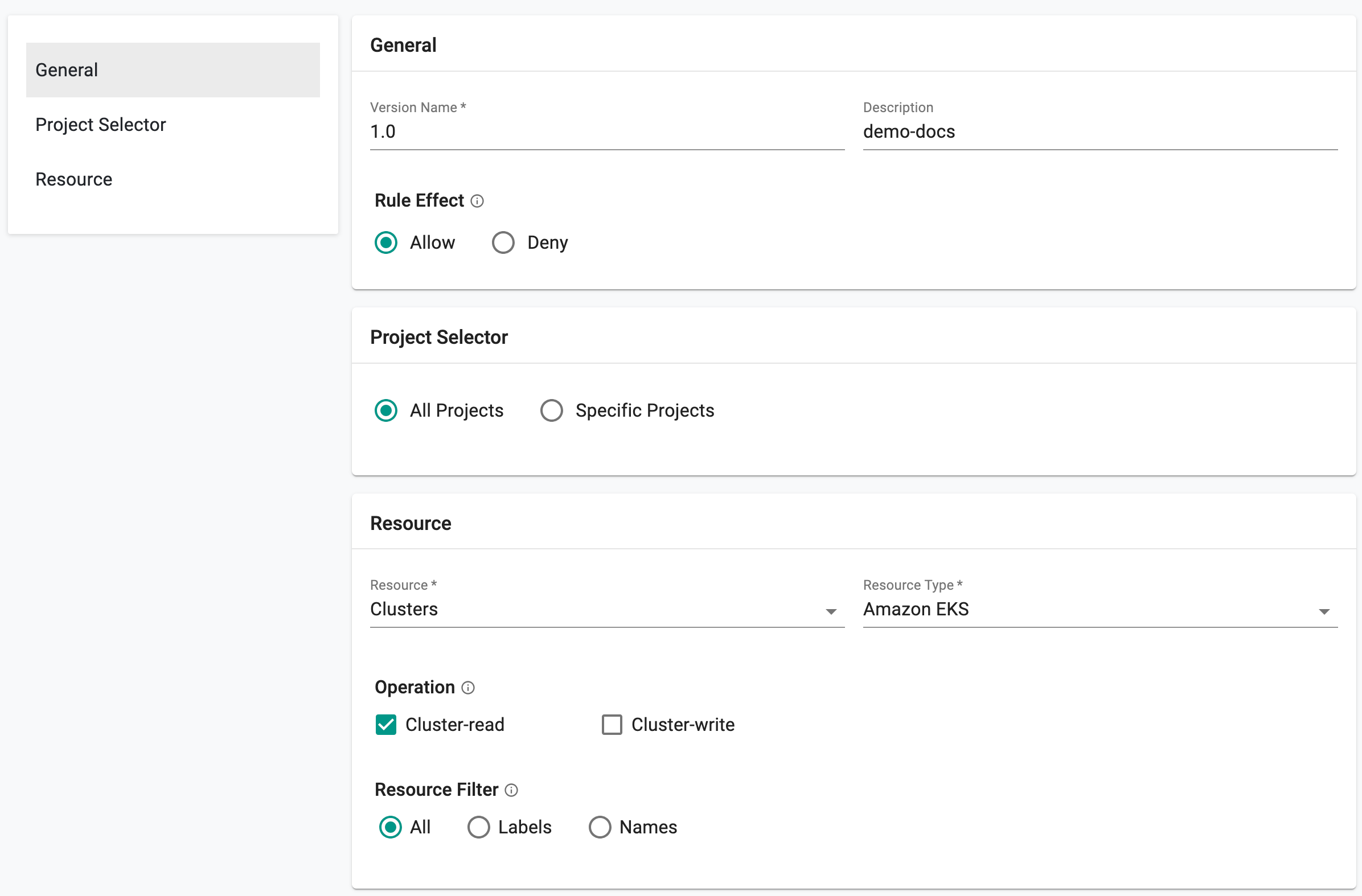
Use Case 1: Allow Amazon EKS Cluster-read¶
The below use case creates a rule with read-only permission for all the EKS clusters
- Provide a version name 1.0 and Rule effect Allow
- Select Resource Clusters and Resource Type Amazon EKS
- Select Operation Cluster-read and Resource Filter All (to give read access to all the EKS cluster details)
- Click Save Changes
- Create an ABAC policy with the above rule
- Create a custom role with base role Namespace Admin (or) Namespace Read Only and attach the above ABAC policy
- Assign this custom role to the required users to apply the permission
Now those users will have only read access to the EKS Clusters and cannot perform actions
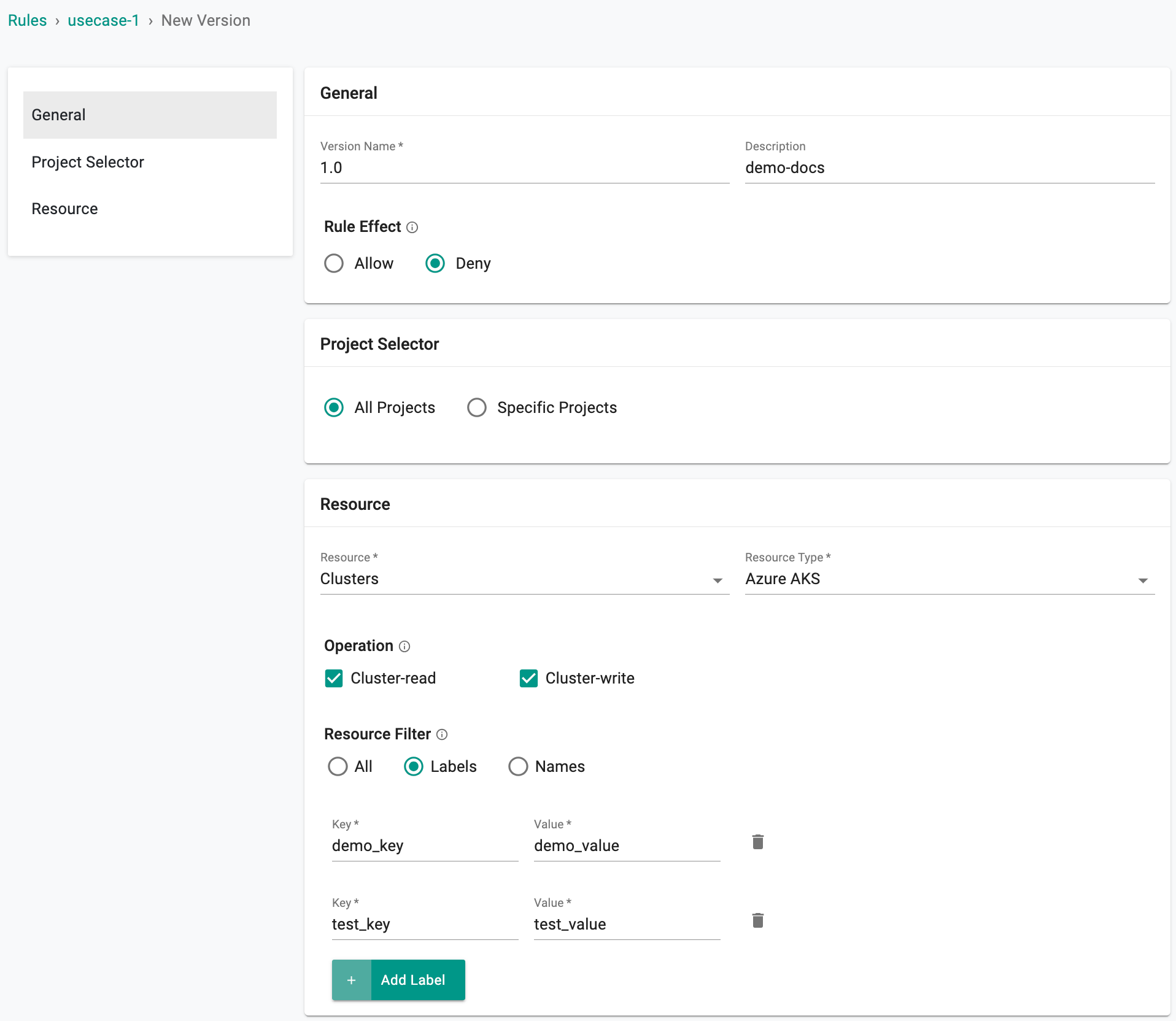
Use Case 2: Deny AKS Cluster label Read/Write access¶
The below use case creates a rule that denies the read/write access to a few AKS Cluster labels
- Provide a version name 1.0 and Rule effect Deny
- Select Resource Clusters and Resource Type Azure AKS
- Select Operation Cluster-read and Cluster-write
- Select Resource Filter Labels and Add Label to add the necessary label keys and values that must be denied
- Click Save Changes
- Create an ABAC policy with the above rule
- Create a custom role with base role Namespace Admin (or) Namespace Read Only and attach the above ABAC policy
- Assign this custom role to the required users to apply the permission
Now those users will not have both read/write access to the specified AKS Cluster labels
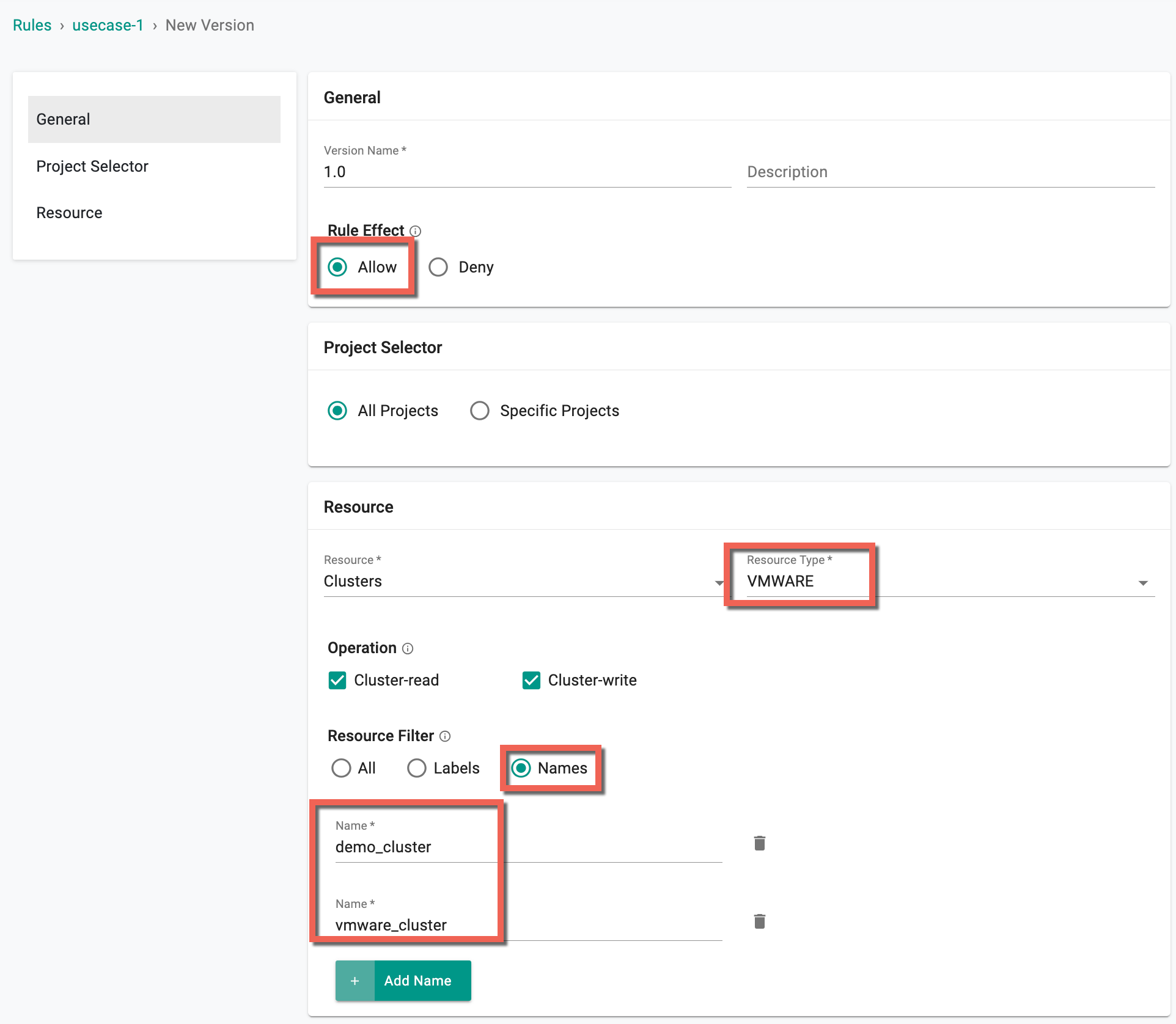
Use Case 3: Allow write access to specific VMWare Clusters¶
The below use case creates a rule that allows read/write access only to a few VMWare clusters
- Provide a version name 1.0 and Rule effect Allow
- Select Resource Clusters and Resource Type VMWARE
- Select Operation Cluster-write
Important
On selecting "write access", read access is granted by default, as "write access" encompasses the highest level of access rights
- Select Resource Filter Names to add the required VMWare cluster Names
- Below is an example of two VMware Clusters "demo_cluster" and "vmware_cluster"
- Click Save Changes
- Create an ABAC policy with the above rule
- Create a custom role with base role Namespace Admin (or) Namespace Read Only and attach the above ABAC policy
- Assign this custom role to the required users to apply the permission
Now those users will have both read/write access only to the VMware Clusters "demo_cluster" and "vmware_cluster"
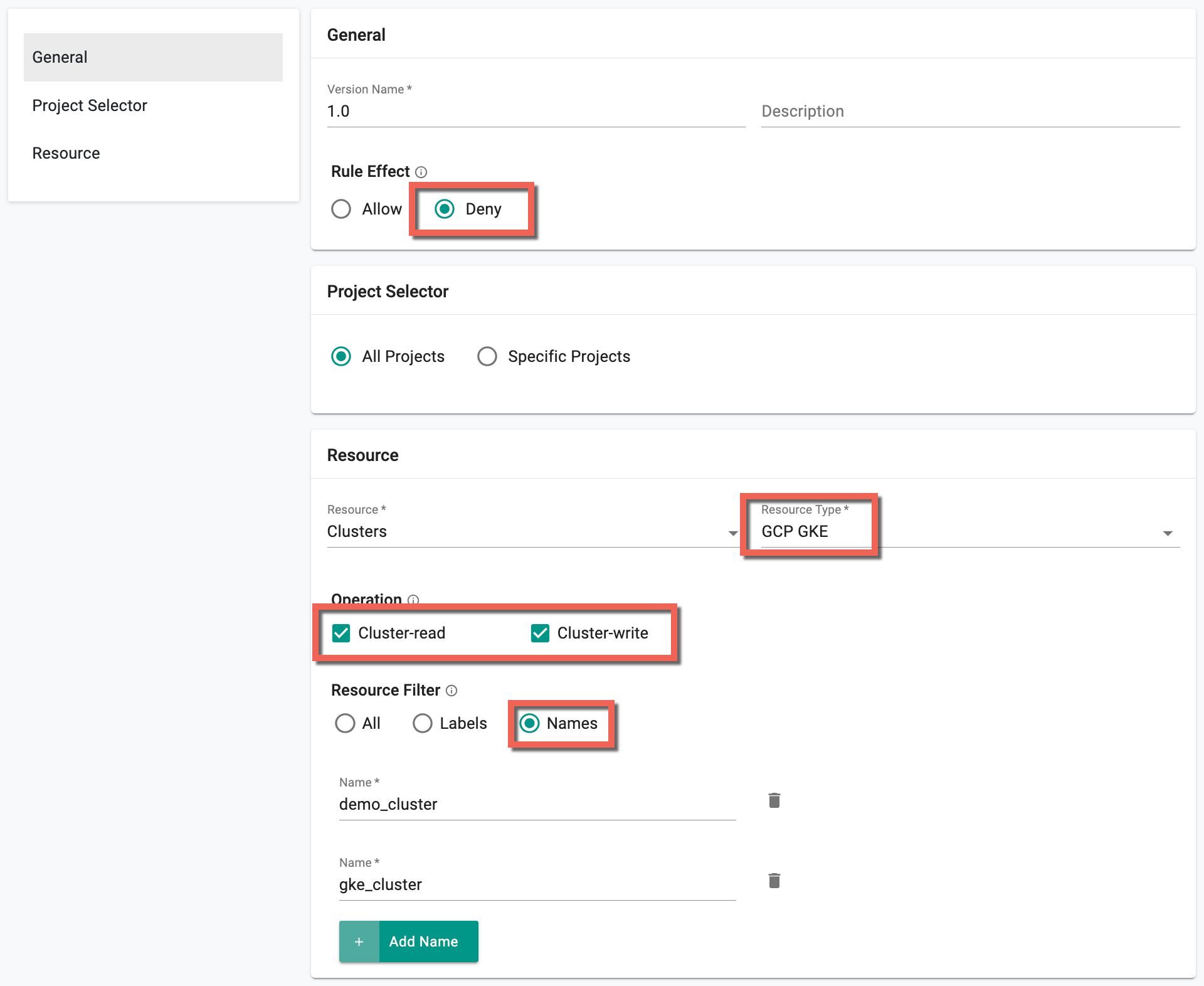
Use Case 4: Deny read/write access to specific GKE Clusters¶
The below use case creates a rule that denies read/write access to a few GKE clusters
- Provide a version name 1.0 and Rule effect Deny
- Select Resource Clusters and Resource Type GCP GKE
- Select Operation Cluster-read and Cluster-write
- Select Resource Filter Names to add the required GKE cluster Names
- Below is an example of two GKE Clusters "demo_cluster" and "gke_cluster"
- Click Save Changes
- Create an ABAC policy with the above rule
- Create a custom role with base role Namespace Admin (or) Namespace Read Only and attach the above ABAC policy
- Assign this custom role to the required users to apply the permission
Now those users will no longer have read/write access to the GKE Clusters named "demo_cluster" and "gke_cluster." However, they will retain access to other GKE clusters, as well as clusters of different types (UPSTREAM, AKS, EKS, etc.).