Setup
What Will You Do¶
This is Part 1 of the self-paced quick start exercise. In this part, you will use the Infra Admin persona to setup and configure the needed resources to use Environment Manager.
Step 1: Import Template¶
In this step, you will use the Loader Utility to import the Environment Manager templates needed for this environment. This process will also setup a System Sync pipeline which will be used to create environment templates.
- Follow the instructions here to use the loader
- When using the loader utility, be sure to use a private repository which will create System Sync pipeline
- When using the loader utility, be sure to uncomment the following template - ../terraform/rafay-aws-resources in the templates section of the values.yaml file
Step 2: Configure Environment Contexts¶
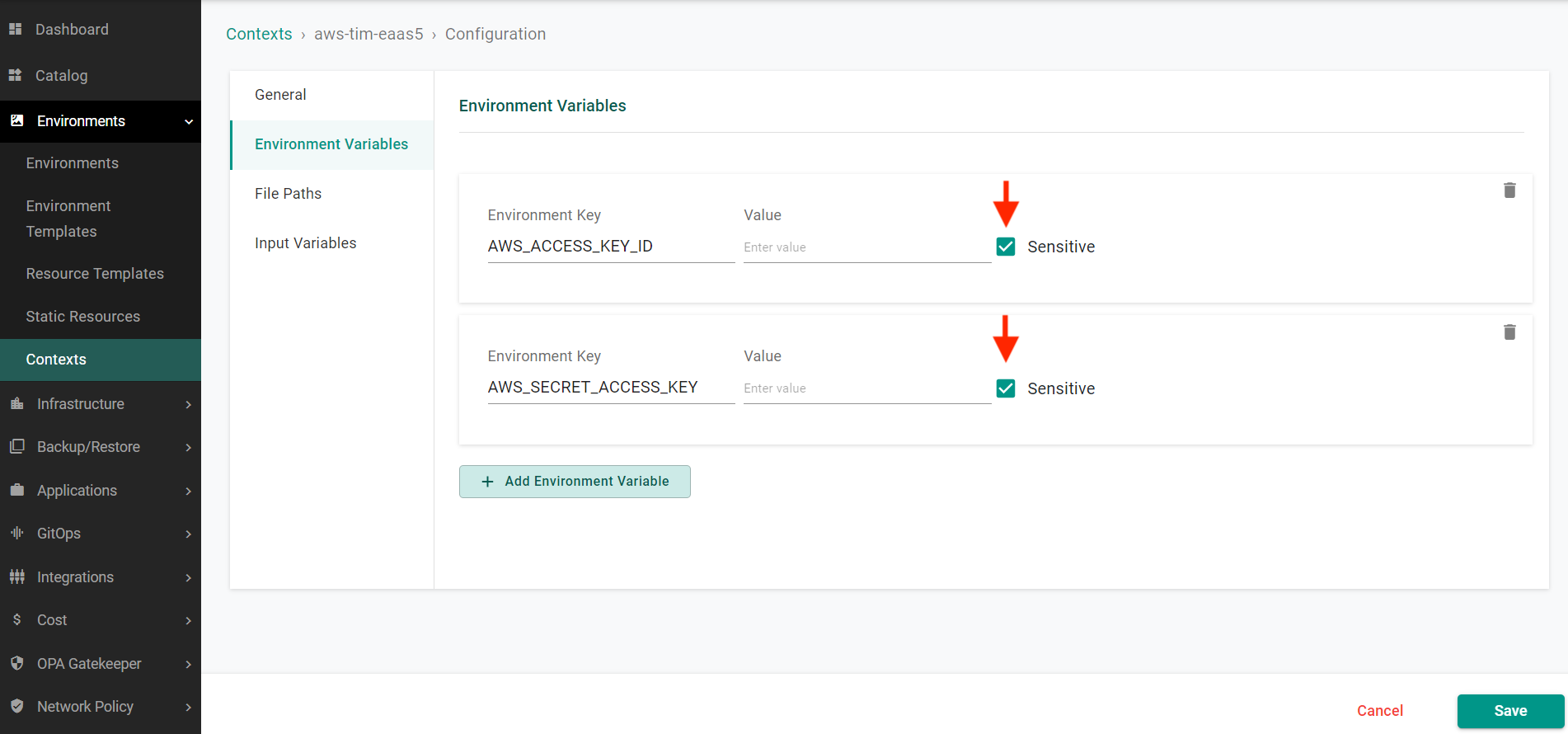
In this step, you will configure an environment context in the controller with your AWS account details. These account details will be used by Environment Manager to interact with your cloud account.
- Log into the controller and select your project
- Navigate to Environments -> Contexts
- Click on the context named rafay-aws-<PROJECT NAME>
- Select Environment Variables
- Populate the values of the variables with the access key and secret for your AWS account
- Ensure that you select the sensitive checkbox for both fields
- Click Save
Important
The Rafay agent automatically writes back the environment variables to Git. The resources (esp. secrets) you identify as sensitive. will be automatically encrypted using a secret sealer before being synced to your Git repo.
Step 3: Configure Resource Template Variables¶
In this step, you will update the resource template for the AWS security group resource. You will be updating specific variables in the resource template to use expressions. The expressions will use the output of the VPC resource template when used together in the same environment template.
- Navigate to Environments -> Resource Templates
- Find and click on the template named rafay-aws-security-group
- Click New Version
- Enter v2 for the version name
-
Navigate to the Input Variables section
-
Update the variable vpc_id with value $(resource["rafay-aws-vpc"].output.vpc_id.value)$
-
Set the value type to Expressions
-
Update the variable
ingress_with_cidr_blockswith the below values
[
{
"from_port": 1433,
"to_port": 1433,
"protocol": "tcp",
"description": "SqlServer access from within VPC",
"cidr_blocks": "$(resource[\"rafay-aws-vpc\"].output.vpc_cidr_block.value)$"
}
]
Step 4: Create VPC and Security Group Environment Template¶
In this step, you will use the System Sync pipeline to create an environment template for the the VPC and security group environment.
- Navigate to your Git repository
- Navigate to <REPO NAME>/rafay-resources/projects/<PROJECT NAME>/environmenttemplates
- Create a new file named vpc-and-security-group.yaml
- Copy the below contents into the file being sure to update the project name and any variable values to match your specific environment
apiVersion: eaas.envmgmt.io/v1
kind: EnvironmentTemplate
metadata:
name: vpc-and-security-group
project: UPDATE_ME
description: Create a VPC and Security Group in AWS
displayName: AWS VPC and Security Group
spec:
iconURL: https://cdn2.iconfinder.com/data/icons/amazon-aws-stencils/100/Non-Service_Specific_copy_Virtual_Private_CLoud_-512.png
readme: "## Introduction\n\nUsers can use this template
to create a VPC and Security Group in AWS \n\n---\n\n##
What does this do behind the scenes? \n\nThis template will perform the following
in a sequence: \n\n1. Create a new VPC in AWS using the name of the environment \n2. Create a Security Group within the VPC using the name of the environment\n \n\n---\n\n## Defaults and Overrides \nUnless specified, the
new VPC will be created with the default settings for the AWS region and subnets. The subnets include private, public and database subnet groups
Users have the option to override the defaults with alternative options. See the input variables section below for complete details. "
resources:
- kind: resourcetemplate
name: rafay-aws-vpc
resourceOptions:
version: v1
type: dynamic
- dependsOn:
- name: rafay-aws-vpc
kind: resourcetemplate
name: rafay-aws-security-group
resourceOptions:
version: v2
type: dynamic
variables:
- name: region
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
value: us-west-2
valueType: text
- name: azs
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
value: '["us-west-2a","us-west-2b","us-west-2c"]'
valueType: hcl
- name: create_database_subnet_group
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
value: "true"
valueType: hcl
- name: public_subnets
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
value: '["10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24", "10.0.3.0/24"]'
valueType: hcl
- name: private_subnets
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
value: '["10.0.4.0/24", "10.0.5.0/24", "10.0.6.0/24"]'
valueType: hcl
- name: database_subnets
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
value: '["10.0.7.0/24", "10.0.8.0/24", "10.0.9.0/24"]'
valueType: hcl
- name: identifier
options:
override:
type: notallowed
required: true
value: $(environment.name)$
valueType: expression
version: v1
versionState: active
- Commit the file to the repository
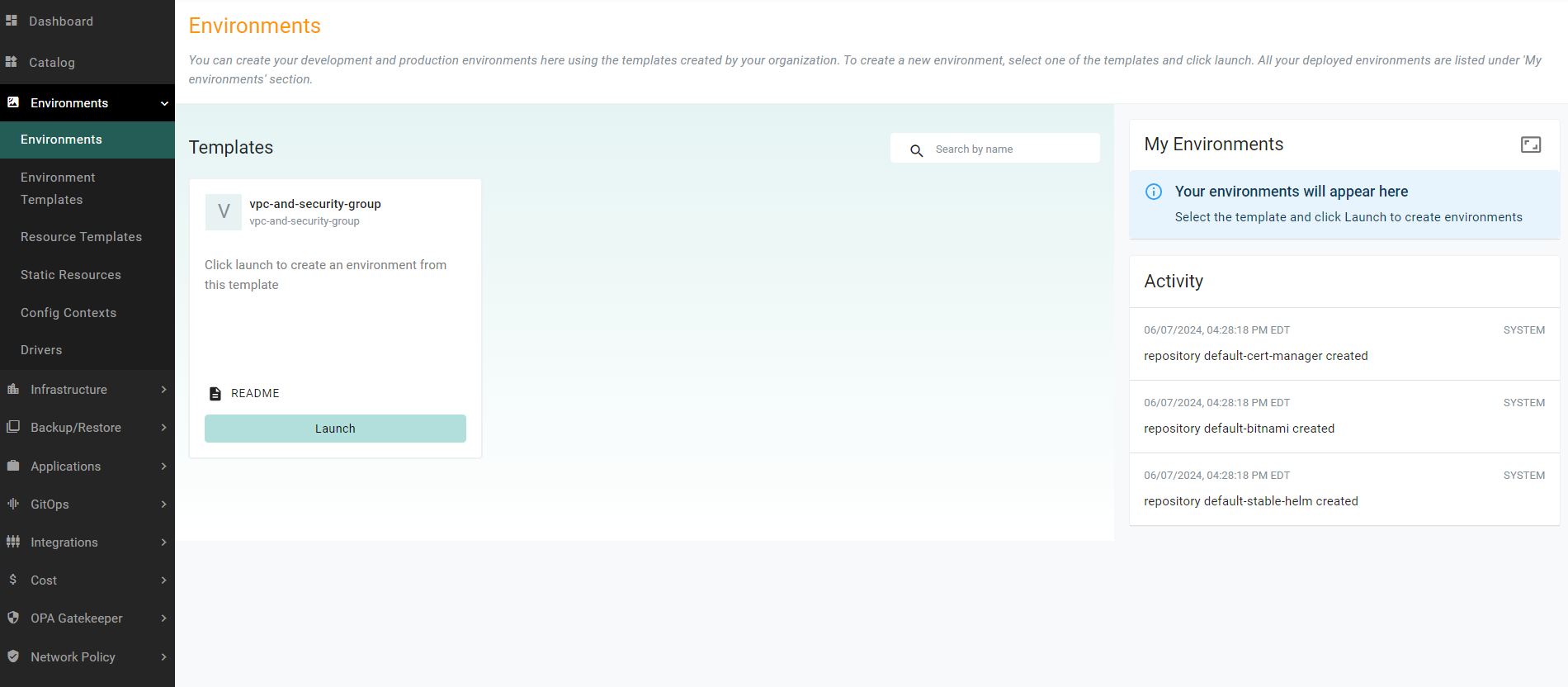
- In the console, navigate to Environments -> Environments to see the environment card named vpc-and-security-group ready to be launched
Step 5: Launch VPC and Security Group Environment¶
In this step, you will use the console to launch the environment. By launching the environment, a VPC and security group will be created in AWS. These resources will be used later in an additional environment template to build other AWS resources.
- Navigate to Environments -> Environments
- Find the card named vpc-and-security-group and click launch
- Enter a name for the environment
- Update any of the parameters if needed
- Click Save & Deploy
After ~5 minutes, the environment will be deployed and the details of the environment resources will be displayed in the Results section of the screen.
Step 6: Create RDS Instance Environment Template¶
In this step, you will use the System Sync pipeline to create an environment template for an RDS Postgres database.
- Navigate to your Git repository
- Navigate to <REPO NAME>/rafay-resources/projects/<PROJECT NAME>/environmenttemplates
- Create a new file named rds.yaml
- Copy the below contents into the file being sure to update the project name, region and any variable values to match your specific environment
- Use the Results section of the vpc-and-security-group environment to obtain the values for the variables vpc_security_group_ids and db_subnet_group_name
apiVersion: eaas.envmgmt.io/v1
kind: EnvironmentTemplate
metadata:
name: rds
project: UPDATE_ME
description: Create a Postgres RDS database in an existing AWS VPC and Security Group
displayName: AWS RDS Postgres Database
spec:
iconURL: https://cloud-icons.onemodel.app/aws/Architecture-Service-Icons_01312023/Arch_Database/64/Arch_Amazon-RDS_64.svg
readme: "## Introduction\n\nUsers can use this template
to create an RDS PostgreSQL Database in AWS within an existing VPC \n\n---\n\n##
What does this do behind the scenes? \n\nThis template will perform the following
in a sequence: \n\n1. Create a new RDS PostreSQL database in AWS within the specified existing VPC\n \n\n---\n\n## Defaults and Overrides \nUnless specified, the
new database will be created with the default settings.
Users have the option to override the defaults with alternative options. See the input variables section below for complete details. "
resources:
- kind: resourcetemplate
name: rafay-aws-rds
resourceOptions:
version: v1
type: dynamic
variables:
- name: region
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: UPDATE_ME
valueType: text
- name: name
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: $(environment.name)$
valueType: expression
- name: engine
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: postgres
valueType: text
- name: engine_version
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "14"
valueType: text
- name: family
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: postgres14
valueType: text
- name: major_engine_version
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "14"
valueType: text
- name: instance_class
options:
override:
restrictedValues:
- db.t3.micro
- db.t3.small
- db.t3.small
- db.t3.large
type: restricted
required: true
value: db.t3.micro
valueType: text
- name: allocated_storage
options:
override:
restrictedValues:
- "20"
- "50"
- "100"
type: restricted
required: true
value: "20"
valueType: text
- name: max_allocated_storage
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "100"
valueType: text
- name: storage_encrypted
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "false"
valueType: text
- name: username
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
valueType: text
- name: port
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "5432"
valueType: text
- name: multi_az
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "false"
valueType: text
- name: maintenance_window
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: Mon:00:00-Mon:03:00
valueType: text
- name: backup_window
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: 03:00-06:00
valueType: text
- name: enabled_cloudwatch_logs_exports
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: '["postgresql", "upgrade"]'
valueType: hcl
- name: create_cloudwatch_log_group
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "true"
valueType: text
- name: backup_retention_period
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "1"
valueType: text
- name: skip_final_snapshot
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "true"
valueType: text
- name: deletion_protection
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "false"
valueType: text
- name: performance_insights_enabled
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "true"
valueType: text
- name: performance_insights_retention_period
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "7"
valueType: text
- name: create_monitoring_role
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "false"
valueType: text
- name: monitoring_interval
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: "0"
valueType: text
- name: parameters
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: |-
[
{
name = "autovacuum"
value = 1
},
{
name = "client_encoding"
value = "utf8"
}
]
valueType: hcl
- name: db_subnet_group_name
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: UPDATE_ME
valueType: text
- name: vpc_security_group_ids
options:
override:
type: notallowed
value: '["UPDATE_ME"]'
valueType: hcl
- name: password
options:
override:
type: allowed
required: true
valueType: text
version: v1
versionState: active
- Commit the file to the repository
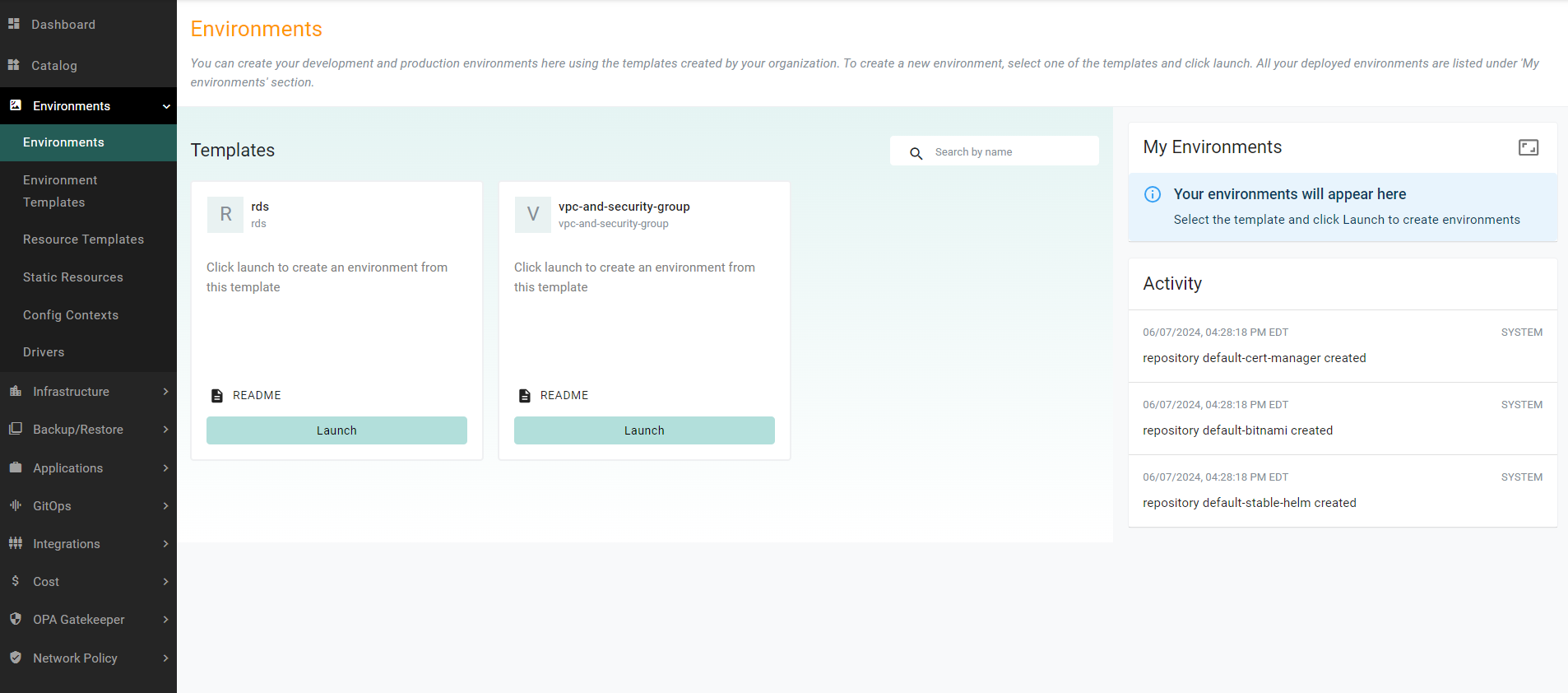
- In the console, navigate to Environments -> Environments to see the environment card named rds ready to be launched
Step 7: Share Environment Template with Self-Service Users¶
In this step, you will share the RDS environment template with the Developer users.
- Ensure the developer users are part of a group that has the Environment Template User role Instructions
- Navigate to Environments -> Environment Templates
- Click the manage sharing icon next to the template named rds
- Select the projects the self-service users are part of
Recap¶
At this point, you have everything setup and configured for self-service users to deploy environments through Environment Manager.