Audit Logging
Audit Logs and Org Admins¶
Audit logs can be seen as a security-relevant chronological record that provide evidence of the sequence of activities that have performed on the system. All changes performed by authorized users of an Org are tracked.
Important
Users of an Org can view information in an audit trail, but cannot delete records from it.
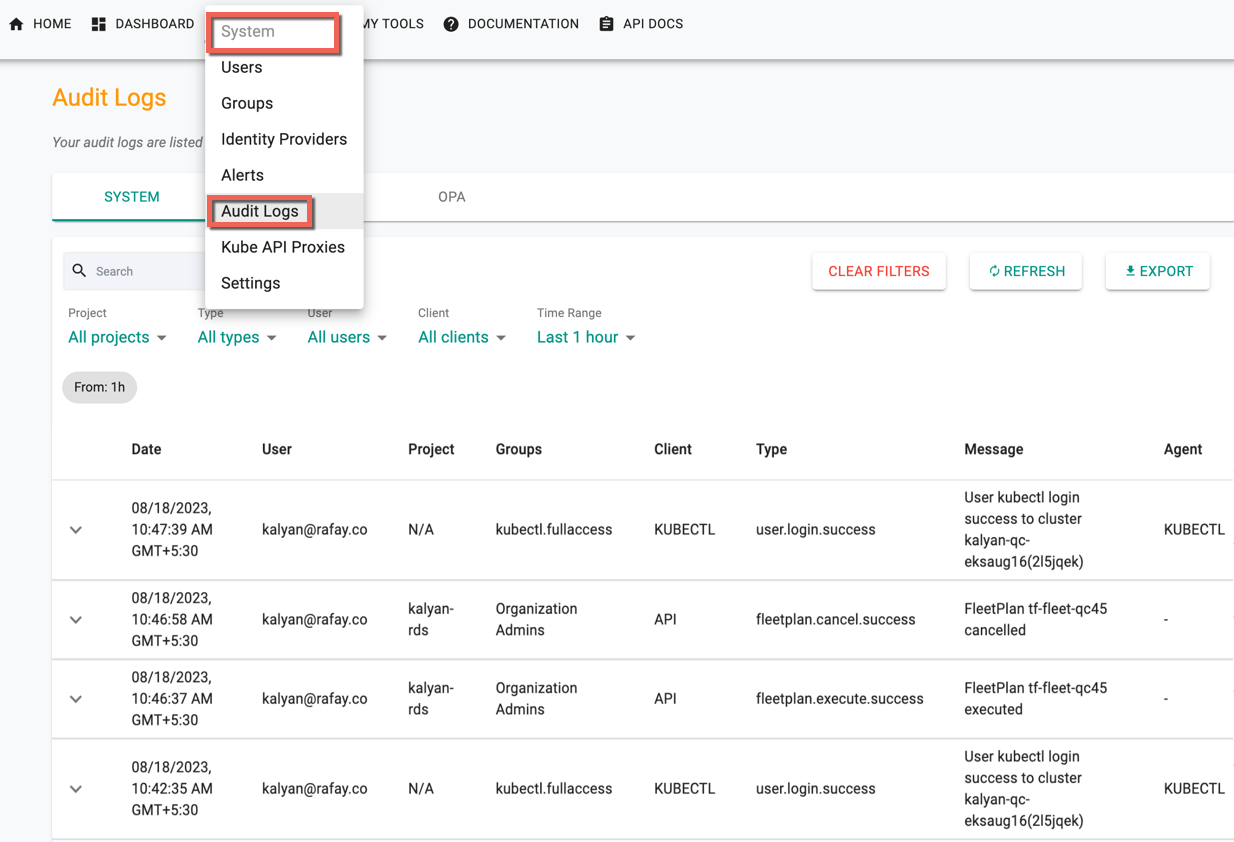
Click System from the Controller menu bar and select Audit Logs to view all actions performed by authorized users of an Org.
System Logs¶
System is the default page of Audit Logs. The system logs contains the entire history of the specific organization and the logs appears sorted by "date/time" i.e. always in a reverse chronological format (latest to older). An illustrative example is shown below.
Node Event Audit Logs¶
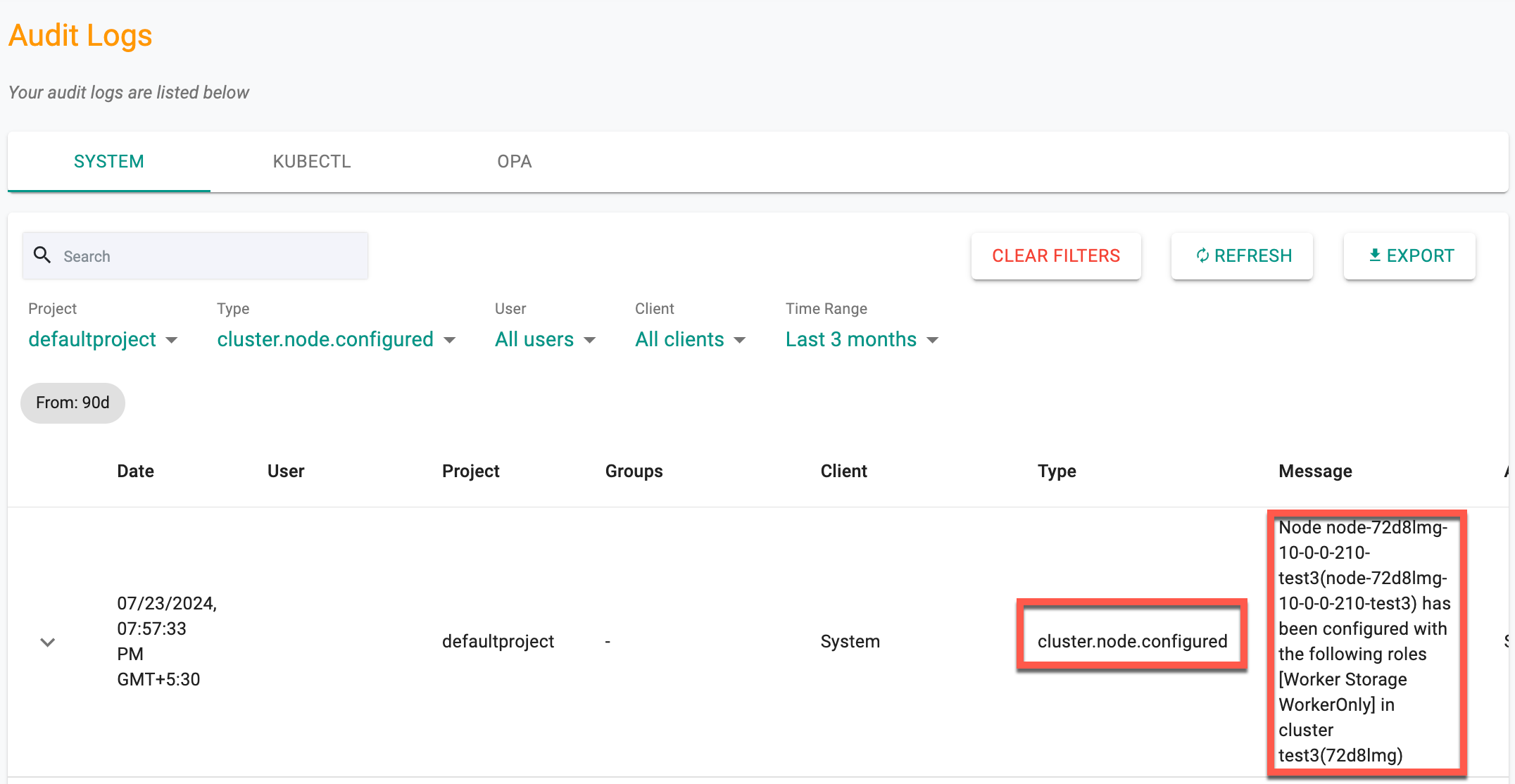
Nodes Events
Audit logs for node events such as DISCOVERED, APPROVED, REJECTED, DELETED, REDISCOVERED, CONFIGURED, and PROVISIONED provide enhanced visibility into node lifecycles. These logs aid in detecting security issues and offer clear audit trails for troubleshooting. Each entry includes a timestamp, node name or ID, cluster name, event type, and a descriptive message. Filtering and searching by node name, cluster name, and event type is essential.
Example of Node Event Log:
CONFIGURED:
- Type: cluster.node.configured
- Message: Node
Filters¶
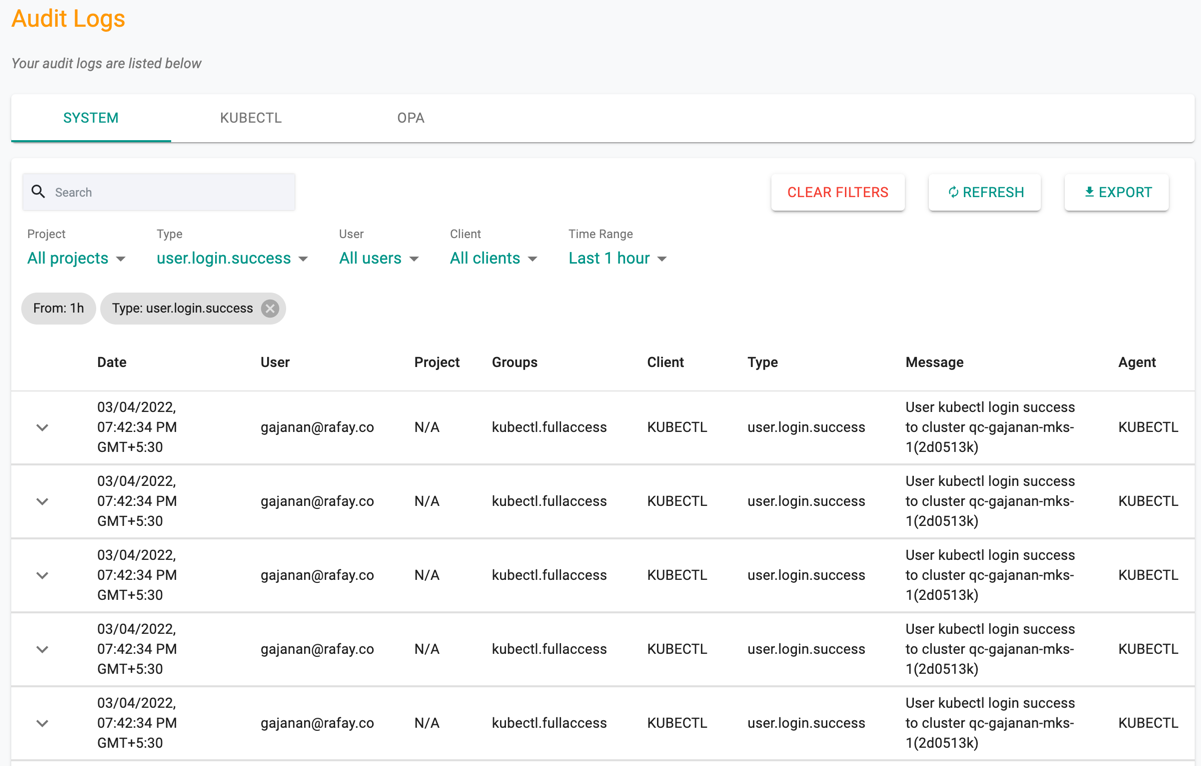
Canned filters are provided so that the audit logs can be filtered and the user can quickly retrieve the required data.
- Project
- Type of action
- User
- Client type: Browser or CLI or KUBECTL
- Time Range
An illustrative example for a filtered view is shown below.
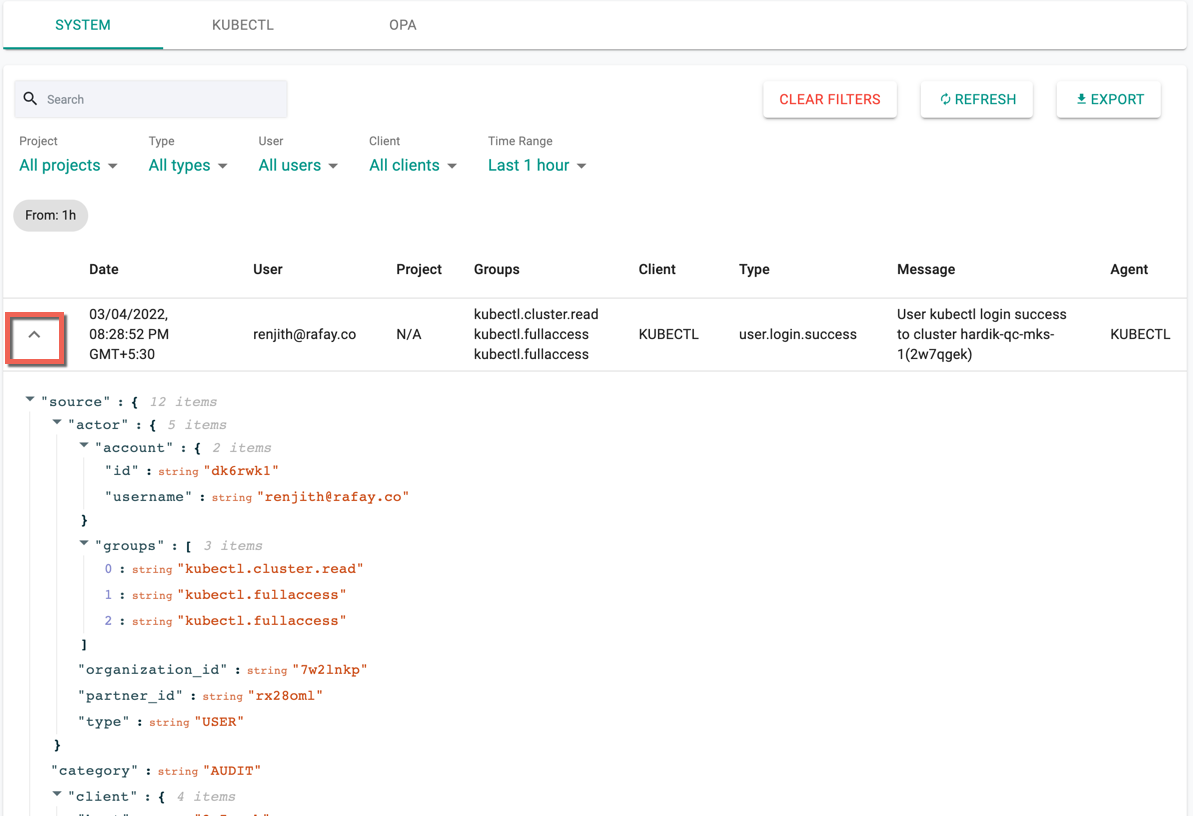
Click the up/down arrow of each log to quickly show/hide the entire JSON payload and this shows all the metadata associated with it
Important
All users with access to specific projects also have visibility into the audit logs, but limited to just the project they have access to.
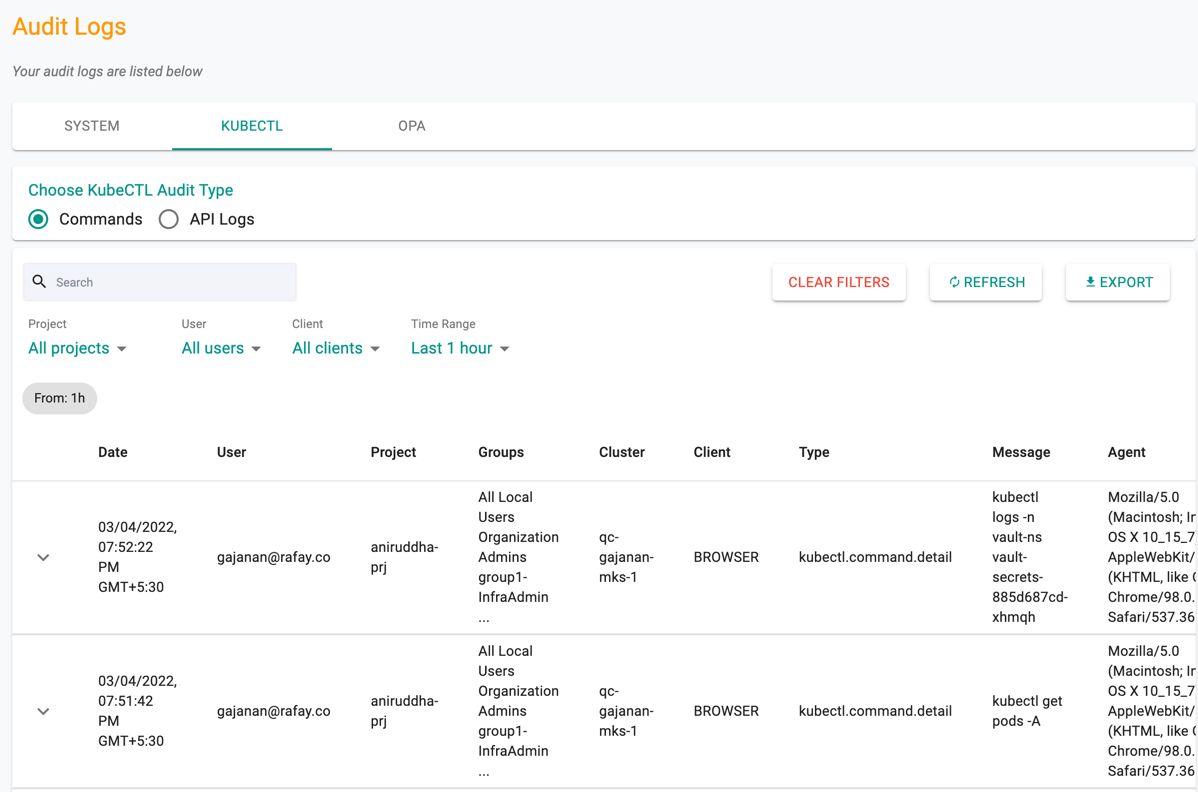
KUBECTL Logs¶
KUBECTL shows the history of commands and API Logs called under each project for various reason(s)
Options
- Search: A free text search box is provided for the users to quickly search for the required log details
- Clear Filters: Remove the applied filters and reset to the default view
- Refresh: Refreshes the page to view the latest audit logs
- Export: Allows the user to download the user's audit log in CSV format
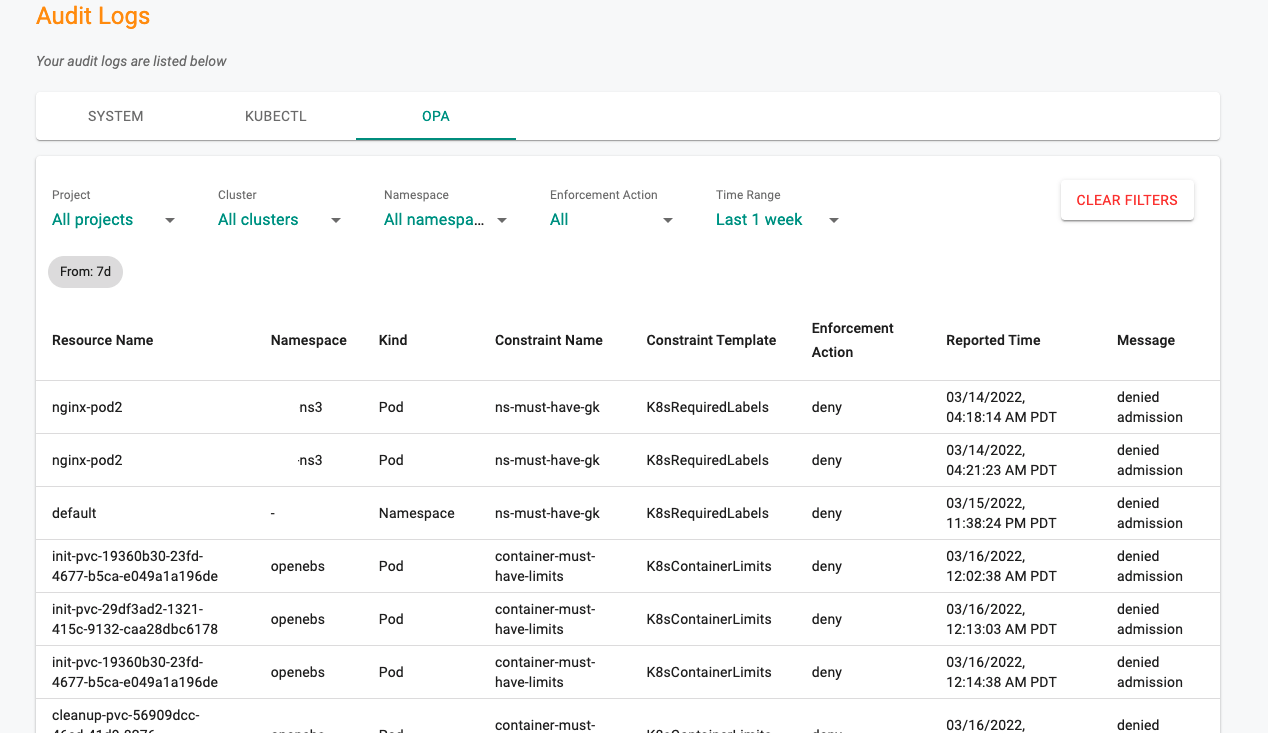
OPA Logs¶
OPA Gatekeeper processes admission requests whenever resources in the clusters are created, updated or deleted. Resources that violate the configured OPA Gatekeeper policy are listed here along with details. Users can filter the data based on the requirement (e.g., Projects, Clusters)
Use Clear Filters to bring back the default data, if any filters applied
Audit Logs in SIEM¶
Customers can configure the audit logs (system, kubectl and OPA violations) from their Org to be streamed to their corporate SIEM platforms to make sure that their security operation teams have deep visibility and insight.
Important
Click here for additional details on how to configure aggregation of audit logs to your corporate SIEM.
Common Use Cases¶
The ability to follow records back to their origin provides numerous benefits, including transparency and a defense of records for compliance, record integrity and accuracy, system protection from misuse or harm, and security of sensitive or vital information.
These are achieved through these four areas:
User Accountability¶
Implementing audit trails promotes appropriate user behavior, which can prevent improper use of information, and unauthorized use or modifications.
In addition, the user knows that their actions are automatically recorded and tied to their unique identity.
Reconstruction of Events¶
When an investigation is warranted or triggered, the first step to remediate a problem is knowing the "when,” the “how," and the "what" of the event. Visibility into this information can aid in problem detection and prevent future occurrences of things such as hacking, system failures, outages, or corruption of information.
Intrusion Detection¶
Audit trails aid in identifying suspicious behavior or actions. Unauthorized access is a serious problem for most systems. Many regulations now have mandates for the security of information and maintaining confidentiality. Protection also extends to intellectual property, designs, personnel information, and financial records.
Operational Issues¶
Through real-time monitoring, you can use automated audit logs to identify problems that indicate system implementation issues, operational issues, unusual or suspicious activities, or system and operator errors.
Retention Period¶
Long term maintenance of audits can prove difficult for many organizations because the logs can occupy extensive storage space that may not be readily available. We will retain the audit trail for 365 days (one calendar year).