Restricted Roles & Identities
Restricted Roles and Identities Required for Creating an AKS Cluster¶
In Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), clusters require an identity to access Azure resources. This identity can either be a managed identity (recommended) or a service principal.
In this discussion, we will delve into bringing your own managed identities and outline the minimum restricted roles and identities needed to create an AKS cluster with Azure Container Registry (ACR) and custom Virtual Network (VNET) configuration.
Another example is if you want to use Azure Monitor to get logs and metrics from your cluster. The pods responsible for this task need to collect logs from the cluster and send them to Azure Monitor. To do this, they need to be authenticated and authorized. One solution is to implement another managed identity to authorize the sending of data to Azure Monitor.
Restricted Roles and Identities¶
When creating a cluster through Rafay Platform with a restricted set of roles, we need the following identities and roles:
- Rafay's Service Principal (SPN): Requires the Contributor role specifically for the cluster resource group.
In addition to this, we need to create managed identities.
For example, if you need to create an AKS cluster with ACR and a custom VNET, you need the following managed identities:
-
Managed Identities:
-
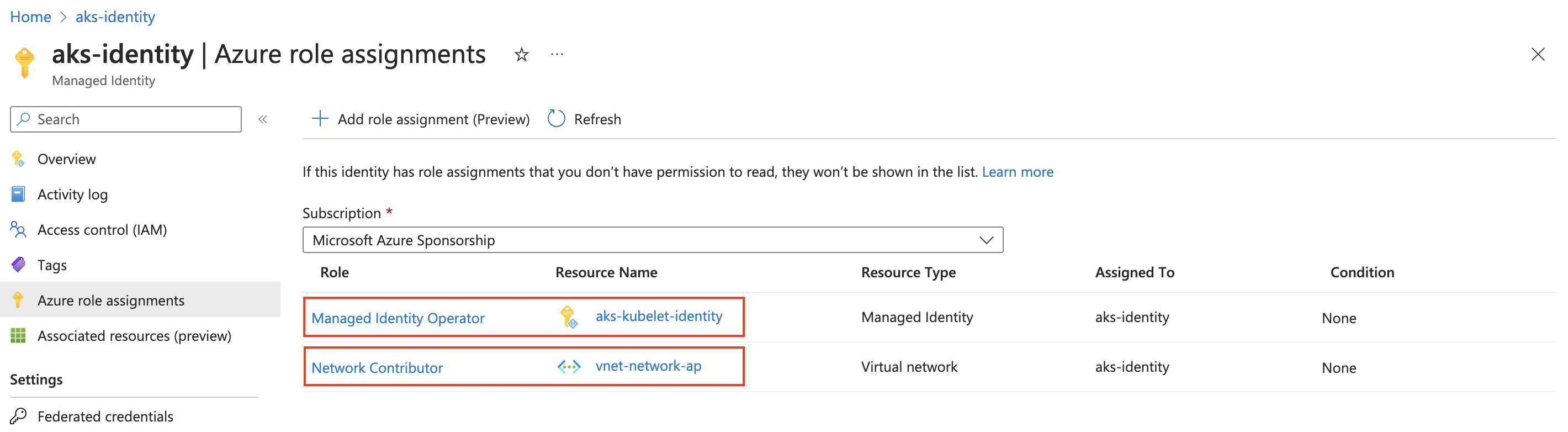
Kubelet Identity: Assign ACR Pull permission to this scoped to the ACRs from which the cluster would pull images.This will be used by kubelet Component, which is why it's called Kubelet identity.
-
Cluster Managed Identity:
- Assign Network Contributor Role to this scoped to the virtual network where the cluster is deployed (this can also be scoped to individual subnets).
- Assign Managed Identity Operator Role to this scoped to the Kubelet Identity that we created previously.
-
After successfully creating the roles and identities on Azure, we need to utilize them in the cluster when it is created through our Rafay controller.
Here is the cluster configuration that you can use as a reference, where a User Assigned identity along with kubelet identity is configured.
- aks-identity: Used for the cluster resource group.
- aks-kubelet-identity: Required for kubelet to Pull from ACR.
apiVersion: rafay.io/v1alpha1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: aks-demo-test2
project: ankurp
spec:
blueprint: default-aks
cloudprovider: demo-ankurp-app
clusterConfig:
apiVersion: rafay.io/v1alpha1
kind: aksClusterConfig
metadata:
name: aks-demo-test2
spec:
managedCluster:
apiVersion: "2022-07-01"
identity:
type: UserAssigned
userAssignedIdentities:
? /subscriptions/a2252eb2-7a25-432b-a5ec-e18eba6f26b1/resourceGroups/ankurpmanaged/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/aks-identity
: {}
location: centralindia
properties:
identityProfile:
kubeletidentity:
resourceId: /subscriptions/a2252eb2-7a25-432b-a5ec-e18eba6f26b1/resourceGroups/ankurpmanaged/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/aks-kubelet-identity
apiServerAccessProfile:
enablePrivateCluster: true
dnsPrefix: aks-demo-test2-dns
kubernetesVersion: 1.27.1
networkProfile:
dnsServiceIP: 10.0.0.10
dockerBridgeCidr: 172.17.0.1/16
loadBalancerSku: standard
networkPlugin: azure
networkPolicy: azure
outboundType: loadBalancer
serviceCidr: 10.0.0.0/16
sku:
name: Basic
tier: Free
type: Microsoft.ContainerService/managedClusters
nodePools:
- apiVersion: "2022-07-01"
location: centralindia
name: primary
properties:
count: 1
enableAutoScaling: true
maxCount: 6
maxPods: 110
minCount: 1
mode: System
orchestratorVersion: 1.27.1
osType: Linux
type: VirtualMachineScaleSets
vmSize: Standard_B4ms
vnetSubnetID: /subscriptions/a2252eb2-7a25-432b-a5ec-e18eba6f26b1/resourceGroups/networkingrg/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/vnet-network-ap/subnets/default1
type: Microsoft.ContainerService/managedClusters/agentPools
resourceGroupName: ankurpmanaged
proxyconfig: {}
type: aks
With the above identities and roles, you will be able to create an AKS cluster with a custom VNET and an ACR, like this: Depending on the specific resources you intend to use, you will need to create the necessary managed identities as outlined in the Azure documentation: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/use-managed-identity.
Authentication and Authorization in AKS¶
When working with AKS, it’s important to understand the different ways users and workloads can authenticate and be authorized to access cluster resources. Below are the main approaches and common issues you may encounter:
1. Local Accounts with Kubernetes RBAC¶
- AKS provides a local admin kubeconfig for direct access.
- Authorization is handled by built-in Kubernetes RBAC.
2. Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) Authentication with Kubernetes RBAC¶
- Authentication is performed via Entra ID.
- Authorization is managed by Kubernetes RBAC.
- Common Error:
Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User “<user-guid>” cannot list resource “pods” in API group "" at the cluster scope - Resolution:
- Identify the Azure AD group (using
admin_group_object_ids) associated with theClusterRoleBindingfor cluster-admin access. - Ensure the Service Principal or user is a member of that Azure AD group.
3. Microsoft Entra ID Authentication with Azure RBAC for Kubernetes Authorization¶
- Authentication is via Entra ID.
- Authorization is managed by Azure RBAC for Kubernetes.
- Common Error:
Error from server (Forbidden): serviceaccounts is forbidden: User “<user-guid>” cannot list resource “serviceaccounts” in API group "" at the cluster scope: User does not have access to the resource in Azure. Update role assignment to allow access - Resolution:
- Navigate to your AKS cluster in the Azure portal.
- Go to the Access control (IAM) section.
- Add a role assignment.
- Select the Azure Kubernetes Service RBAC Cluster Admin role.
- Under Members, choose your Service Principal.
- Save the assignment.
This ensures the service principal has the appropriate RBAC permissions to manage Kubernetes resources through Azure RBAC.